The Evolving Landscape of Vertical Integration: A Deep Dive into Vine Jobs
Related Articles: The Evolving Landscape of Vertical Integration: A Deep Dive into Vine Jobs
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Evolving Landscape of Vertical Integration: A Deep Dive into Vine Jobs. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Evolving Landscape of Vertical Integration: A Deep Dive into Vine Jobs
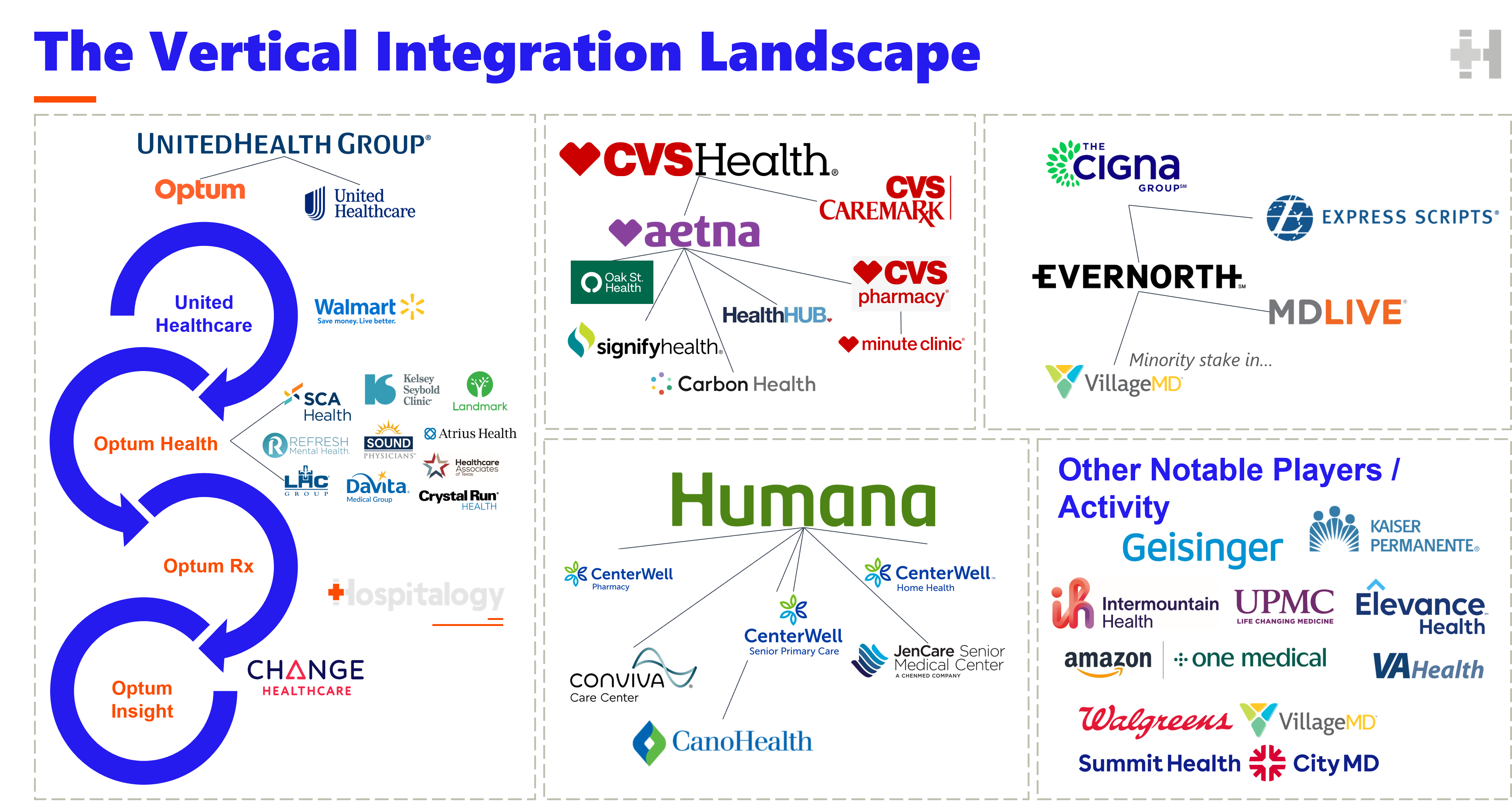
The term "vine jobs" refers to a specific type of employment structure within the agricultural industry, where workers are employed directly by a vertically integrated company. This model stands in contrast to the traditional, fragmented system where farmers, processors, and retailers operate independently.
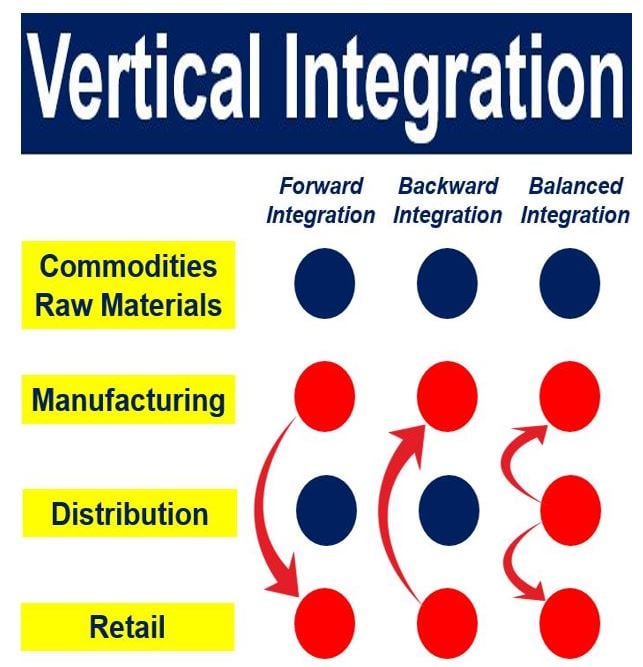
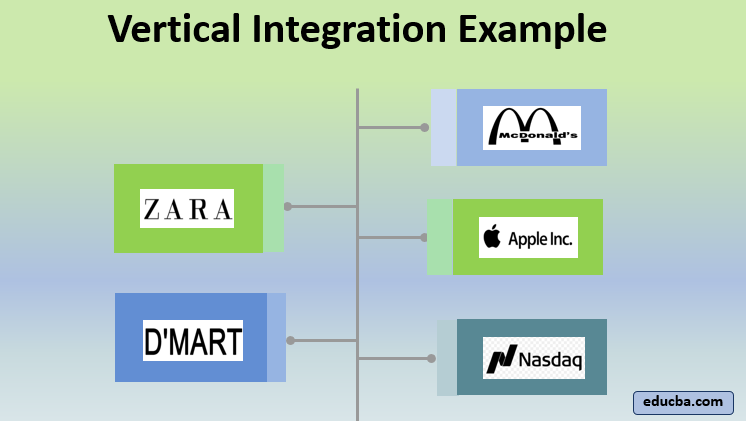
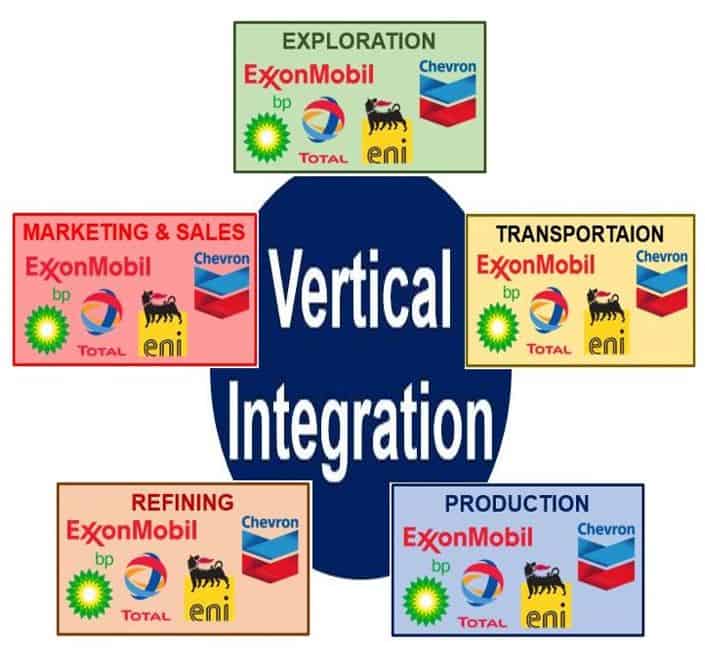
Understanding Vertical Integration
Vertical integration is a business strategy where a company controls multiple stages of the production process. In the context of agriculture, this means a single entity may handle everything from planting and harvesting to processing, packaging, and distribution. This model is becoming increasingly prevalent, driven by several factors, including:
- Efficiency and Cost Reduction: By streamlining the supply chain and eliminating intermediaries, vertically integrated companies can achieve significant cost savings and improve efficiency.
- Quality Control: Vertical integration allows for greater control over the entire production process, ensuring consistent quality and meeting specific customer demands.
- Increased Profitability: Controlling multiple stages of the supply chain can lead to higher profit margins, as the company captures value at each stage.
- Enhanced Brand Recognition: Vertically integrated companies can develop stronger brand recognition by controlling the entire process from farm to table.
Vine Jobs: A Closer Look
Vine jobs, within this vertically integrated framework, represent a shift in the traditional agricultural employment landscape. These jobs offer a unique set of advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages:
- Job Security: Vine jobs often provide greater job security compared to traditional farm work, as they are less susceptible to seasonal fluctuations and market volatility.
- Competitive Wages and Benefits: Vertically integrated companies often offer competitive wages, benefits packages, and opportunities for career advancement.
- Training and Development: These companies often invest in training and development programs for their employees, equipping them with valuable skills and knowledge.
- Improved Working Conditions: Vine jobs frequently involve improved working conditions, including access to modern equipment, safety protocols, and employee support systems.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Flexibility: Vine jobs often require adherence to strict schedules and work protocols, which may limit flexibility for employees.
- Potential for Monotony: The repetitive nature of some tasks within a vertically integrated system can lead to monotony for some employees.
- Limited Career Advancement Opportunities: While some companies offer career advancement opportunities, the scope for vertical mobility may be limited compared to other sectors.
The Impact of Vine Jobs on the Agricultural Workforce
The rise of vine jobs has a significant impact on the agricultural workforce:
- Attracting and Retaining Talent: Vine jobs, with their potential for better wages, benefits, and job security, can attract and retain a more skilled and experienced workforce.
- Shifting Skills Demand: As vertical integration increases, the demand for agricultural workers with specialized skills, such as processing, packaging, and logistics, will rise.
- Increased Unionization: The concentration of workers in vertically integrated companies can lead to increased unionization efforts, potentially impacting working conditions and wages.
FAQs about Vine Jobs
1. What are the typical roles found in vine jobs?
Vine jobs encompass a wide range of roles, including:
- Farm Workers: Planting, harvesting, and tending crops.
- Processing Workers: Handling and processing agricultural products.
- Packaging Workers: Packing and labeling products for distribution.
- Logistics Workers: Managing transportation and warehousing.
- Quality Control Specialists: Ensuring product quality and safety.
- Management and Supervision: Overseeing various aspects of the production process.
2. Are vine jobs suitable for everyone?
While vine jobs offer advantages, they may not be suitable for everyone. Individuals who prefer flexibility, variety in their work, or a high degree of autonomy may find traditional farming or other sectors more appealing.
3. What are the future prospects of vine jobs?
The future of vine jobs is likely to be shaped by several factors, including:
- Technological Advancements: Automation and robotics are likely to play a larger role in agricultural production, potentially impacting the nature and number of vine jobs.
- Consumer Preferences: Growing consumer demand for sustainable and ethical agricultural practices may influence the structure of vine jobs.
- Government Policies: Policies related to labor standards, environmental regulations, and agricultural subsidies can impact the growth and development of vine jobs.
Tips for Success in Vine Jobs
- Develop Relevant Skills: Focus on acquiring skills related to agriculture, processing, packaging, logistics, and quality control.
- Seek Training and Education: Enroll in training programs or pursue higher education to enhance your knowledge and skills.
- Network and Build Relationships: Connect with individuals in the agricultural industry to gain insights and explore opportunities.
- Stay Updated on Industry Trends: Keep abreast of technological advancements, market trends, and regulatory changes affecting the agricultural sector.
Conclusion
Vine jobs represent a significant shift in the agricultural employment landscape. By offering greater job security, competitive wages, and opportunities for career advancement, these jobs can attract and retain a more skilled and experienced workforce. However, it is essential to recognize the potential limitations associated with these roles, such as limited flexibility and potential for monotony. As the agricultural sector continues to evolve, understanding the dynamics of vine jobs is crucial for individuals seeking careers in this vital industry.

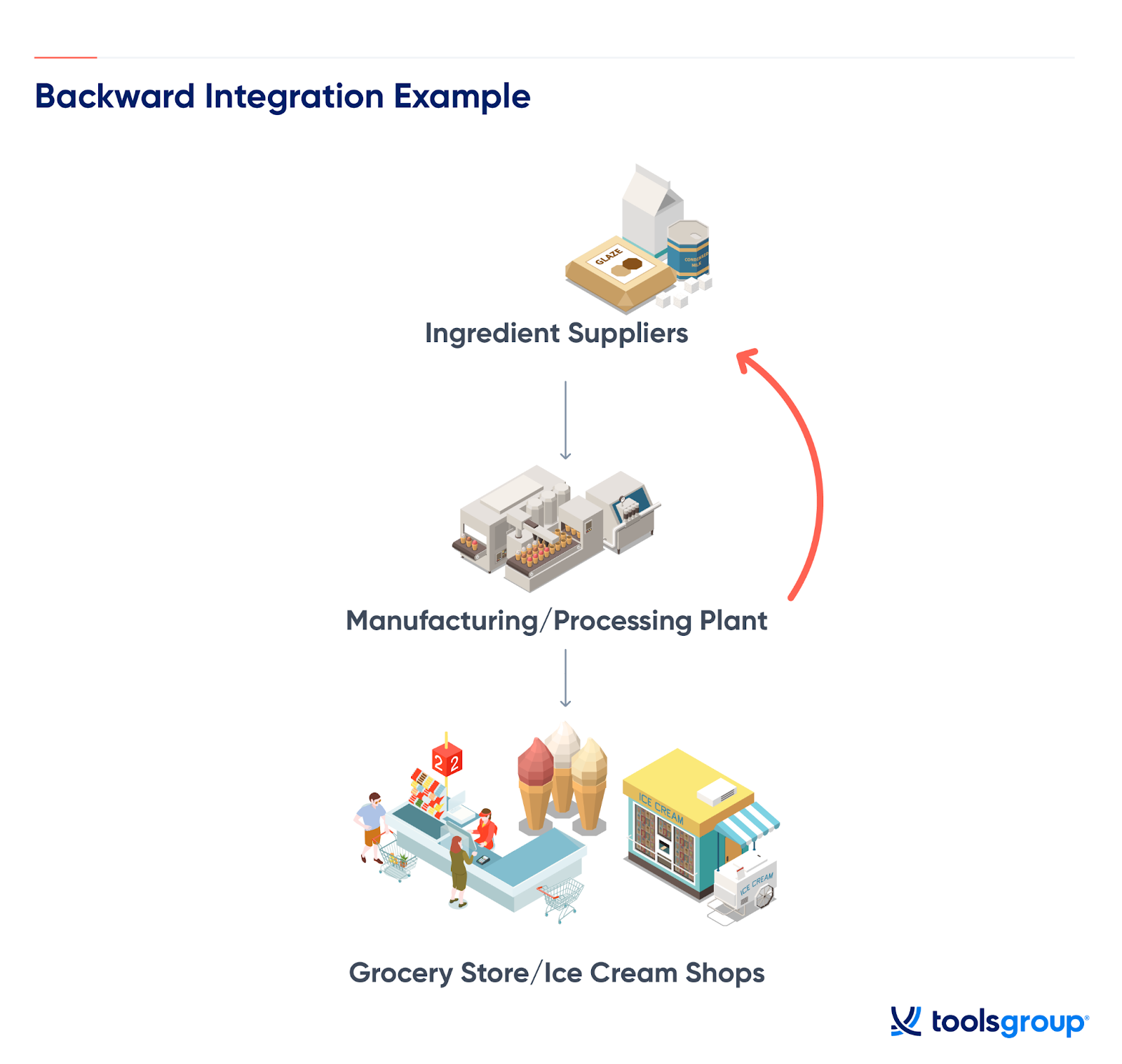
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Vertical-integration-7a31b884b9564a139c5ec2f7885ff3f0.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Evolving Landscape of Vertical Integration: A Deep Dive into Vine Jobs. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
