The Significance of Unionized Employment in the 21st Century: A Comprehensive Exploration
Related Articles: The Significance of Unionized Employment in the 21st Century: A Comprehensive Exploration
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Significance of Unionized Employment in the 21st Century: A Comprehensive Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Significance of Unionized Employment in the 21st Century: A Comprehensive Exploration

The landscape of employment has undergone significant transformation in the 21st century, marked by technological advancements, globalization, and a shifting power dynamic between employers and employees. In this evolving context, the role of labor unions has become increasingly crucial, offering a vital platform for workers to advocate for their rights and secure fair working conditions. This article delves into the multifaceted world of unionized employment, examining its historical significance, present-day relevance, and future prospects.
A Historical Perspective: The Genesis of Unionization
The concept of labor unions emerged in response to the harsh realities of early industrialization. The Industrial Revolution, while ushering in unprecedented technological progress, also created exploitative working conditions characterized by long hours, low wages, and hazardous environments. Workers, lacking individual bargaining power, sought collective strength through the formation of unions.
The earliest unions focused on specific trades, such as the craft guilds of medieval Europe. However, the rise of mass production in the 19th century gave rise to industrial unions, encompassing workers across various sectors. These unions played a pivotal role in advocating for worker rights, including the establishment of minimum wages, the reduction of working hours, and the implementation of safety regulations.
The Modern Union Landscape: Navigating a Complex World
The 20th century witnessed a surge in union membership, reaching its peak in the mid-1950s in the United States. However, the latter half of the century saw a decline in unionization, attributed to factors such as globalization, technological advancements that led to automation, and legislative changes that weakened union power.
Despite this trend, labor unions remain a powerful force in many sectors, particularly in industries like public education, healthcare, and transportation. They continue to advocate for workers’ interests, striving to improve wages, benefits, and working conditions.
The Benefits of Unionized Employment: A Multifaceted Perspective
The benefits of unionized employment extend beyond the immediate gains of higher wages and improved benefits. They encompass a broader range of advantages, impacting both individual workers and the broader economy.
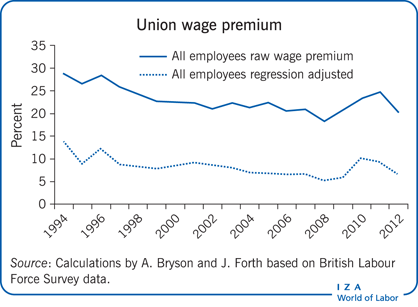
- Improved Wages and Benefits: Unionized workers consistently earn higher wages and enjoy more comprehensive benefits packages compared to their non-union counterparts. These benefits often include health insurance, paid time off, retirement plans, and other forms of compensation.
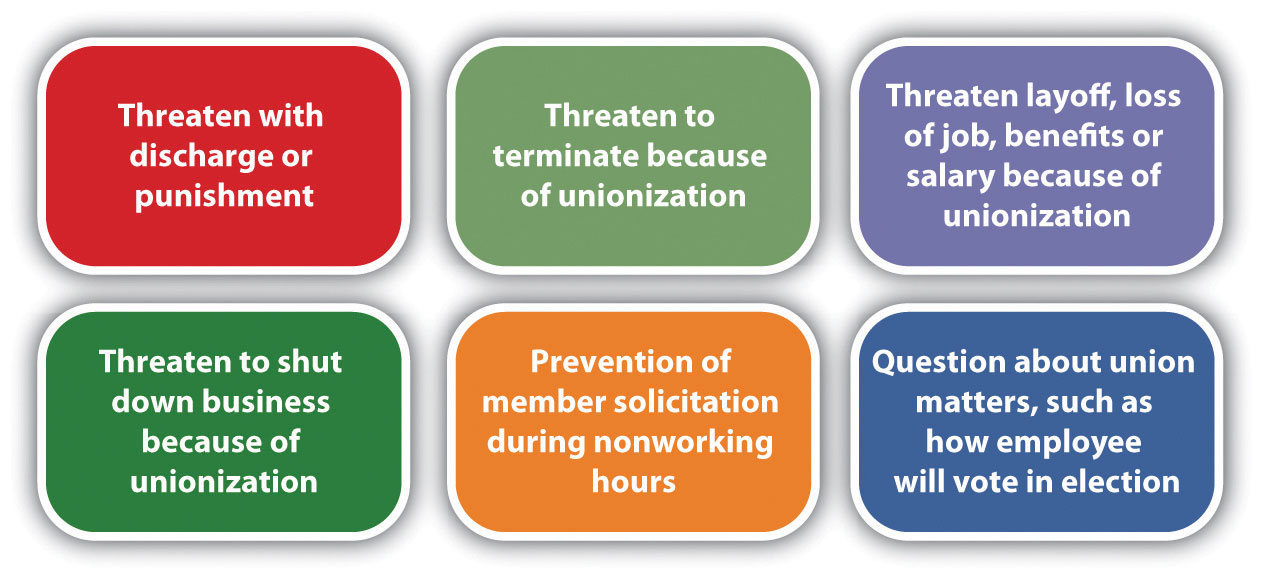
- Enhanced Job Security: Unions play a critical role in protecting workers from arbitrary dismissals and unfair treatment. They advocate for robust grievance procedures, ensuring that employees have avenues to address workplace concerns and seek redress for unfair practices.
- Safer Working Environments: Unions actively push for the implementation of safety regulations and standards, creating safer working environments for their members. They advocate for the provision of appropriate safety equipment, training, and procedures, minimizing the risk of workplace accidents and injuries.
- Increased Workplace Democracy: Unionized workplaces foster a greater sense of workplace democracy, allowing workers to have a voice in decisions that affect their working lives. This participation can range from collective bargaining over wages and benefits to contributing to workplace policies and procedures.
- Strengthened Collective Bargaining Power: By uniting workers, unions create a collective bargaining power that allows them to negotiate on an equal footing with employers. This collective strength enables workers to secure better terms of employment and ensure fair treatment.
- Economic Stability and Growth: Unions contribute to economic stability by advocating for policies that support workers’ rights and promote fair labor practices. They also advocate for investments in infrastructure and education, contributing to long-term economic growth.
Challenges and Opportunities: The Future of Unionization
While unionized employment offers substantial benefits, it also faces significant challenges in the 21st century. The rise of the gig economy, the increasing prevalence of non-standard work arrangements, and the growing influence of automation pose challenges to traditional union models.
However, unions are adapting to these challenges by expanding their outreach to include workers in the gig economy and other non-traditional employment sectors. They are also embracing new technologies and strategies to engage with members and advocate for their interests in the digital age.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Unionized Employment
1. What are the key differences between union and non-union jobs?
Unionized jobs typically offer higher wages, more comprehensive benefits, greater job security, and stronger protections against unfair treatment compared to non-union jobs. Unionized workplaces also generally have more robust grievance procedures and employee participation in decision-making processes.
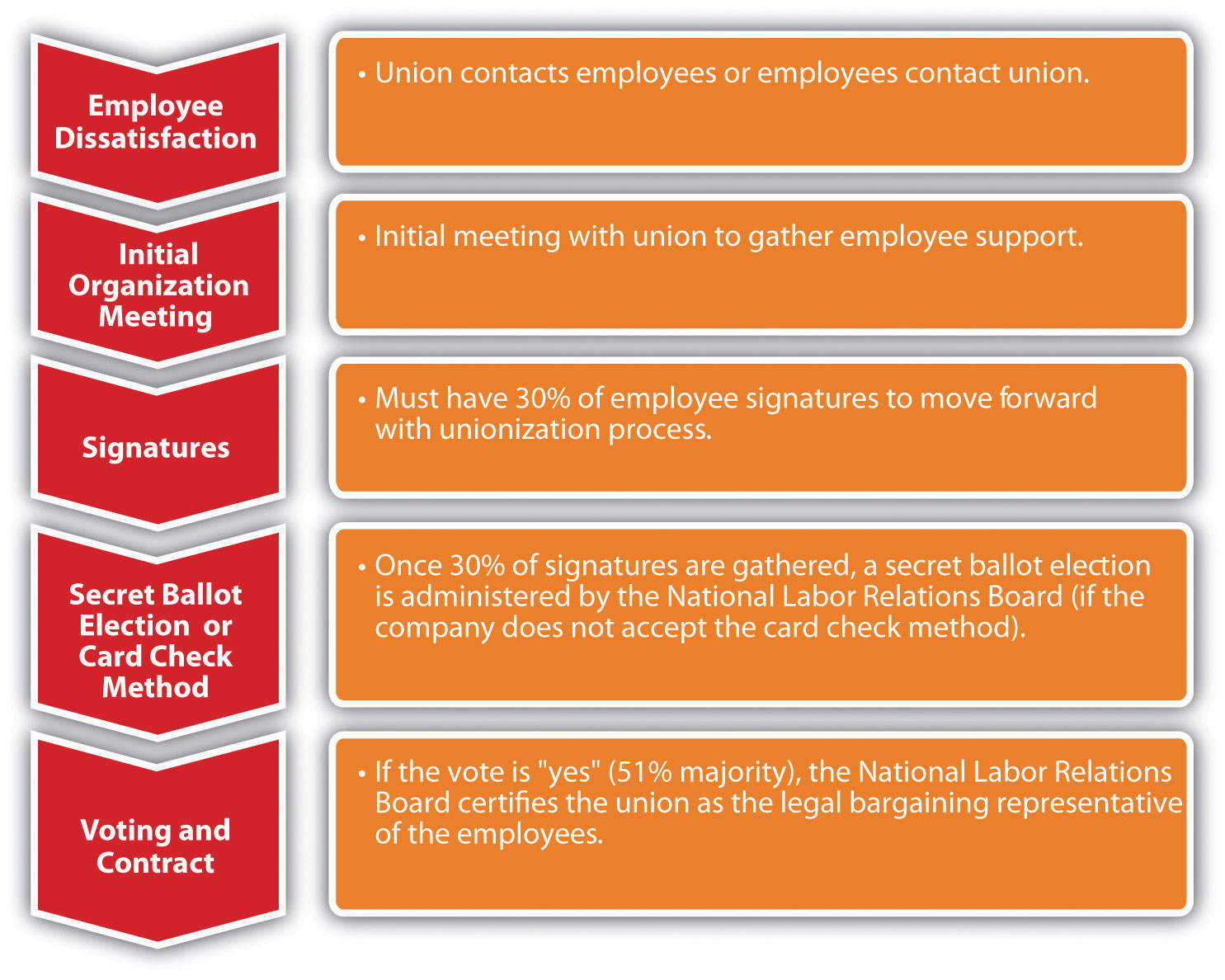
2. How do I join a union?
The process of joining a union varies depending on the specific union and industry. Typically, you can contact the union representing workers in your industry or workplace and inquire about membership requirements and procedures.
3. Are there any downsides to working in a unionized environment?
While unionized jobs offer numerous advantages, there are potential downsides. These may include higher union dues, potential limitations on individual bargaining, and potential for bureaucratic processes in addressing workplace issues.
4. What are the current trends in unionization?
While union membership has declined in recent decades, there are signs of renewed interest in unionization, particularly among younger workers and those in the gig economy. Unions are adapting to these trends by expanding their outreach and exploring new models of organizing.
5. How do unions impact the broader economy?
Unions contribute to economic stability by advocating for policies that support workers’ rights and promote fair labor practices. They also advocate for investments in infrastructure and education, contributing to long-term economic growth.
Tips for Workers Considering Unionized Employment
- Research different unions: Explore unions representing workers in your industry or workplace to understand their specific benefits, membership requirements, and track record.
- Engage with current union members: Talk to workers who are already part of a union to gain firsthand insights into their experiences and perspectives.
- Understand your rights: Familiarize yourself with the legal protections and rights afforded to unionized workers.
- Participate in union activities: Engage in union meetings, events, and activities to stay informed and contribute to the collective effort.
- Advocate for fair treatment: Speak up for your rights and advocate for fair treatment in the workplace, both individually and collectively.
Conclusion: The Enduring Relevance of Unionized Employment
In an era marked by rapid technological advancements, globalization, and evolving employment dynamics, the role of labor unions remains critical. They provide a vital platform for workers to advocate for their rights, secure fair working conditions, and contribute to a more equitable and prosperous society. While facing challenges, unions are adapting to the changing landscape of work, embracing new strategies and technologies to ensure their continued relevance in the 21st century. By understanding the benefits and complexities of unionized employment, workers can make informed decisions about their career paths and contribute to a more just and sustainable future of work.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Significance of Unionized Employment in the 21st Century: A Comprehensive Exploration. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
