The Uneven Landscape of Lockdown: Examining Who Benefits and Who Bears the Burden
Related Articles: The Uneven Landscape of Lockdown: Examining Who Benefits and Who Bears the Burden
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Uneven Landscape of Lockdown: Examining Who Benefits and Who Bears the Burden. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Uneven Landscape of Lockdown: Examining Who Benefits and Who Bears the Burden

The term "lockdown" has become synonymous with the global response to the COVID-19 pandemic. While its implementation has been widespread, its impact has not been uniform. This article delves into the complex question of who benefits from lockdown measures and who shoulders the disproportionate burden, highlighting the uneven landscape of its effects.
The Advantages of Lockdown: A Closer Look
For certain groups, lockdown measures have demonstrably provided advantages, contributing to a sense of safety and security.
1. Healthcare Professionals: Lockdown measures, particularly social distancing and stay-at-home orders, have played a critical role in slowing the spread of the virus. This has alleviated pressure on healthcare systems, enabling medical professionals to manage the influx of patients more effectively. By reducing the overall caseload, lockdown measures have helped to prevent healthcare systems from being overwhelmed, ensuring that critical resources remained available for those most in need.
2. Vulnerable Populations: Lockdown measures have provided crucial protection for vulnerable populations, including the elderly, those with underlying health conditions, and immunocompromised individuals. These groups are at a higher risk of severe illness and death from COVID-19. By limiting social interaction and reducing the potential for exposure, lockdown measures have significantly reduced the risk of infection and hospitalization among vulnerable populations.
3. Environmental Protection: The reduction in economic activity and transportation during lockdowns has had a positive impact on the environment. Air quality has improved in many urban areas, with reductions in emissions of pollutants such as nitrogen dioxide and particulate matter. This has resulted in cleaner air and a decrease in respiratory illnesses, particularly among vulnerable populations.
4. Increased Digital Engagement: Lockdowns have accelerated the adoption of digital technologies, particularly in areas like education, healthcare, and commerce. This has resulted in greater access to online services and resources, expanding opportunities for remote work, learning, and communication.
The Disproportionate Burden: A Critical Examination
While lockdown measures have provided advantages for some, they have also had a significant and disproportionate impact on others, exacerbating existing inequalities and creating new challenges.
1. Economic Disparity: Lockdowns have had a devastating impact on the global economy, leading to job losses, business closures, and a decline in economic activity. This has disproportionately affected low-income earners, gig workers, and those in industries heavily reliant on physical interaction, such as hospitality and tourism. The loss of income has resulted in increased poverty, food insecurity, and homelessness, further widening the gap between the wealthy and the poor.
2. Mental Health Strain: The social isolation, uncertainty, and disruption caused by lockdowns have taken a toll on mental health. Increased rates of anxiety, depression, and substance abuse have been reported, particularly among children, adolescents, and those already struggling with mental health issues. The lack of access to support networks and mental health services has exacerbated these challenges, highlighting the need for increased investment in mental health resources.
3. Education Disruption: School closures have disrupted the education of millions of children and adolescents worldwide. While online learning platforms have provided alternative access to education, they have not been able to replace the in-person experience for all students. This has particularly affected students from low-income families, who may lack access to technology and adequate learning environments at home. The long-term impact of these disruptions on educational attainment and future opportunities remains a significant concern.
4. Domestic Violence: Lockdowns have been linked to an increase in domestic violence, as victims are confined at home with their abusers, with limited access to support services and resources. The increased stress and tension within households, coupled with the lack of escape routes, have created a dangerous environment for victims of domestic violence.
Who Does Lockdown Work For? An Uneven Distribution of Benefits and Burdens
The evidence suggests that lockdown measures have provided benefits for certain groups, such as healthcare professionals, vulnerable populations, and the environment. However, the negative impacts of lockdowns have fallen disproportionately on low-income earners, those with pre-existing mental health conditions, children and adolescents, and victims of domestic violence.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
Q: Are lockdowns truly necessary to control the spread of the virus?
A: The effectiveness of lockdowns in controlling the spread of COVID-19 has been the subject of ongoing debate. While they have undoubtedly played a role in reducing transmission rates, the relative effectiveness of different measures and their impact on various social and economic factors remain complex and require further research.
Q: What are the long-term consequences of lockdowns?
A: The long-term consequences of lockdowns are still unfolding, and their full impact is yet to be understood. The economic, social, and psychological effects of these measures will continue to be studied and debated in the years to come.
Q: How can we mitigate the negative impacts of lockdowns?
A: Mitigating the negative impacts of lockdowns requires a multifaceted approach. This includes targeted economic support for vulnerable populations, increased investment in mental health services, ensuring access to education for all students, and strengthening support systems for victims of domestic violence.
Tips for Navigating Lockdown Measures
1. Stay Informed: Remain informed about the latest public health guidelines and recommendations.
2. Practice Self-Care: Prioritize mental and physical health by engaging in activities that promote well-being, such as exercise, meditation, and connecting with loved ones.
3. Seek Support: Reach out to friends, family, or mental health professionals if you are struggling with the challenges of lockdown.
4. Advocate for Change: Support initiatives that address the inequities and negative impacts of lockdown measures.
Conclusion: A Call for Equity and Resilience
Lockdown measures have been a necessary tool in the fight against COVID-19, but their implementation has been uneven, with certain groups benefiting while others shoulder a disproportionate burden. Moving forward, it is crucial to acknowledge the uneven landscape of lockdown impacts and prioritize equity in policy responses. This requires targeted interventions to address the specific needs of vulnerable populations, a focus on long-term recovery, and a commitment to building a more resilient and equitable society.

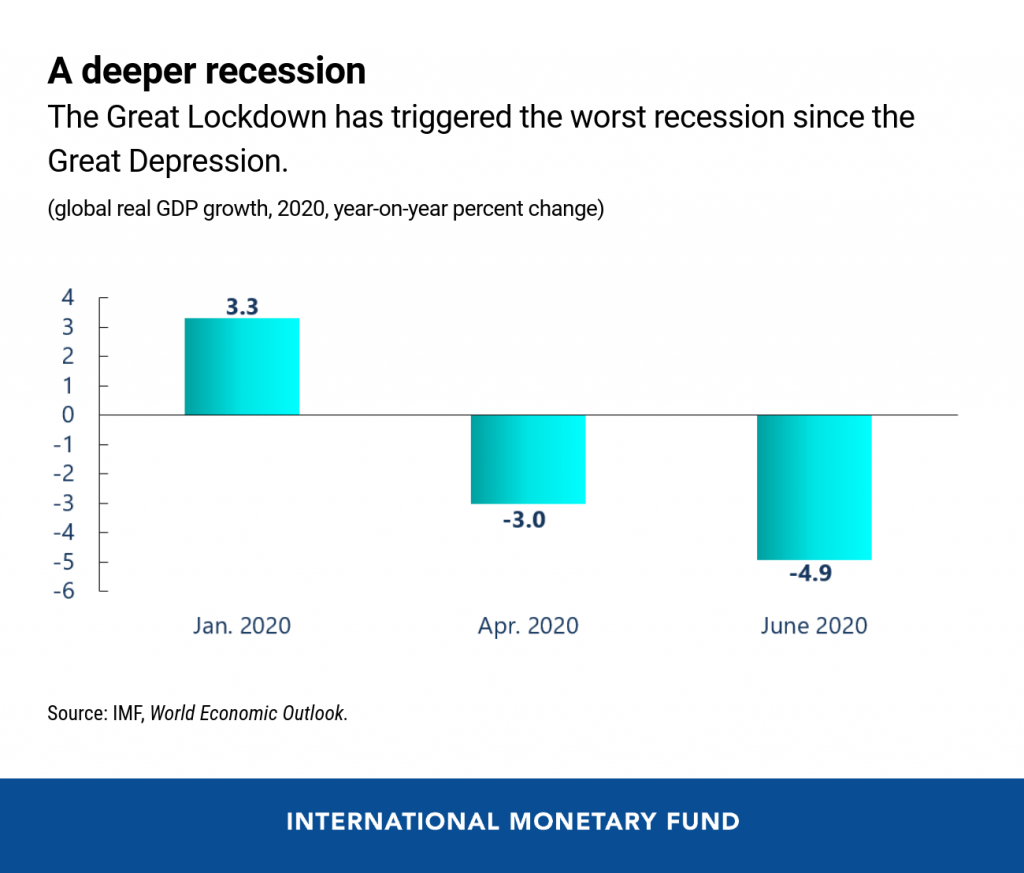
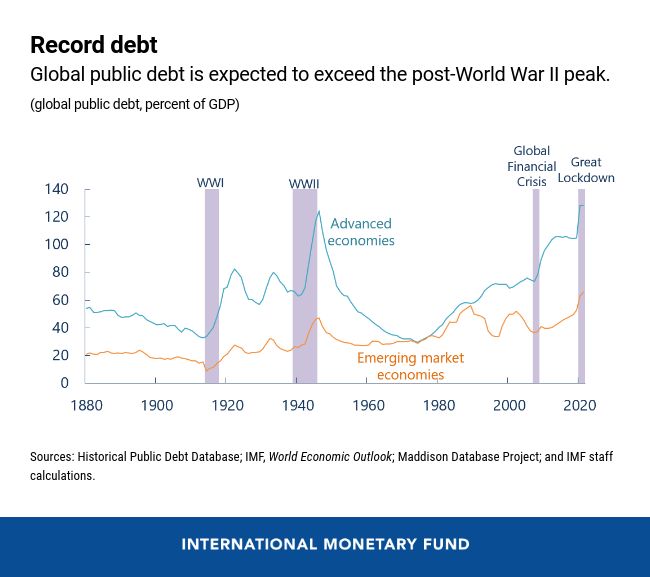
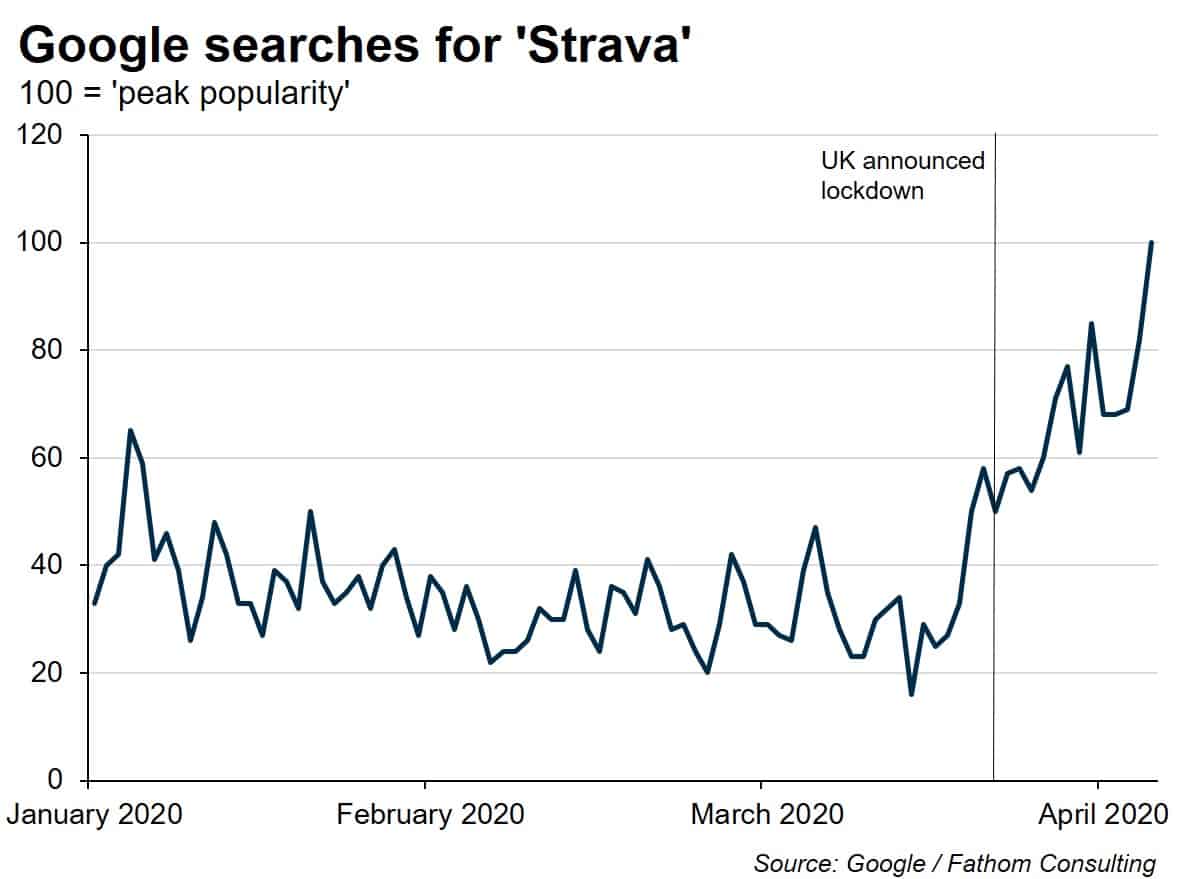
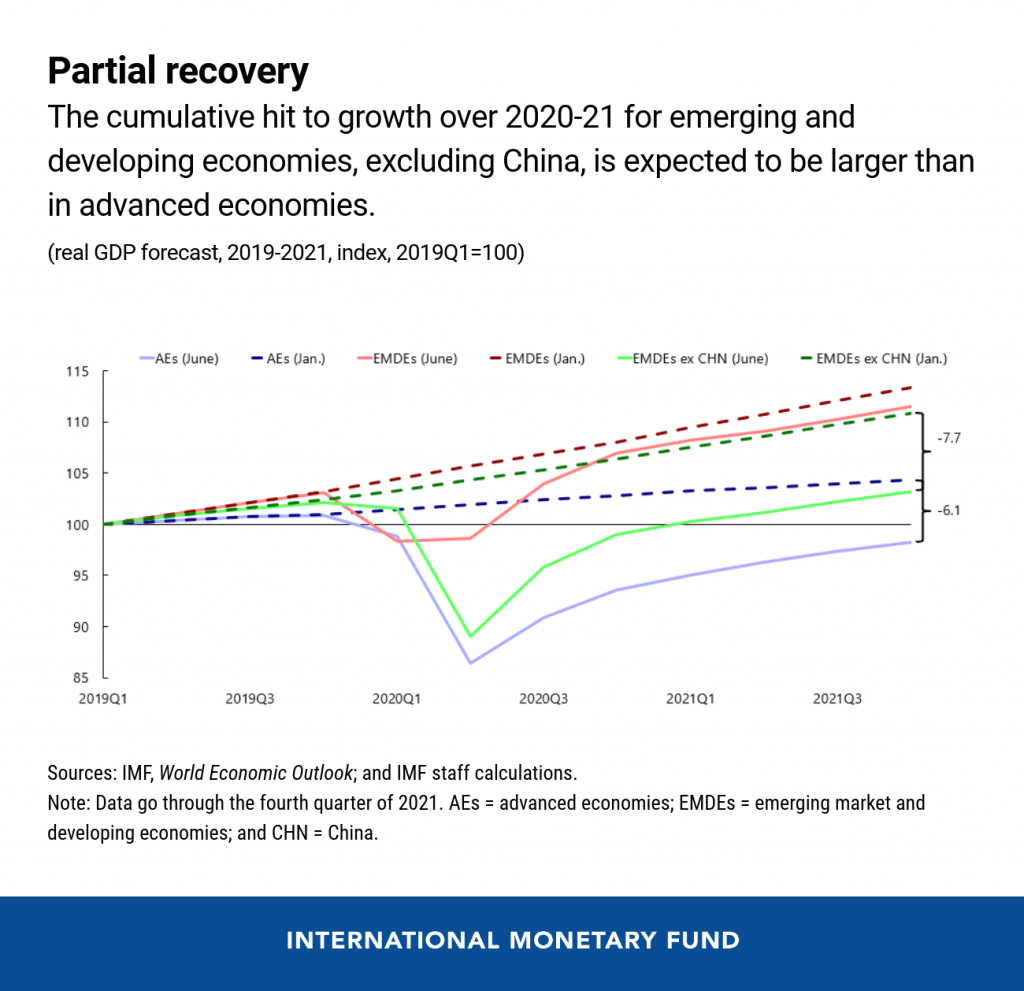
![]()


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Uneven Landscape of Lockdown: Examining Who Benefits and Who Bears the Burden. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
